Visual impairment
When we talk about visual impairment we mean the total or partial loss of the ability of a subject to perform, in total autonomy, the simple and recurring actions of daily life that require the support and contribution provided by the visual field.
These deficits can affect:
- visual acuity: in this case the subject is not able to distinguish the details that characterize an object. Visual acuity is also called visus and is measured by the optician or ophthalmologist.
- amplitude of the field of view: in normal conditions, it has a total amplitude of about 120 in the vertical plane and 180 in the horizontal one.
Visual deficits encompass all those problems that affect both with the vision and with the visual field. However, a distinction is made between blindness and low vision if one or both eyes are involved.
Follow us in this scientific excursus to stay up to date on innovative cures and treatments brought forward by research.
Specialized doctors will enrich this in-depth study of visual impairment through interviews, statements and articles, thus providing a valuable contribution to the dissemination of topics on which they can boast years of study and research.
Latest articles

Multiple sclerosis and visual symptoms
It is one of the most common and most serious chronic diseases of the central nervous system that in 30% of cases begins with visual disorders.

Hemianopsia test: methods and examination instruments
Evaluation of hemianoptic disorder is a complex process that aims to reduce difficulties and counteract limitations due to the deficit.

Optic ataxia: what it is, causes and symptoms
Optic ataxia is a coordination deficit between the visual and motor areas. What deficits it can cause and how to diagnose it.

Parkinson’s disease and visual impairment
Parkinson’s disease and visual disturbances: an in-depth look at the visual deficits affecting Parkinson’s patients.

Optic chiasm: what are the problems associated with its lesion
The optic chiasm represents the junction through which direct visual information passes to the brain.

Lazy eye or amblyopia: symptoms, causes and treatments
The lazy eye or amblyopia is a reduced visual ability of an eye compared to the contralateral eye.

Squint: types, symptoms and treatments
The causes of this problem are numerous, each of which contributes to describe the characteristic features of the various types of squint.

Diplopia: what are the causes and cures
Causes, symptoms and treatment of “Double Vision” or Diplopia.
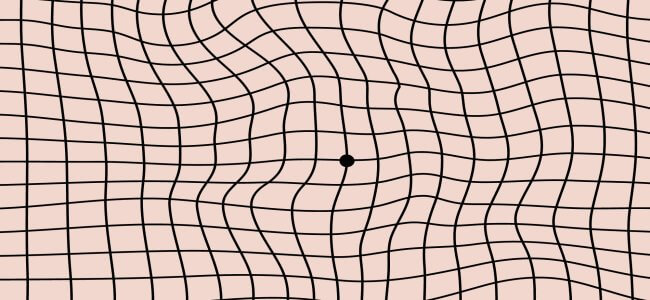
Maculopathy: symptoms, causes and various types
The term maculopathy is used to refer to multiple pathologies, which entail various symptoms, but this issue may be difficult to recognize at first, since the initial stages are usually asymptomatic.

The aqueous humour: how is it involved in glaucoma
The aqueous humour has many functions (nutrient, pressure stabilization and refraction) within the ocular structure.

Neglect: what is it, how to recognize it and how to cure it
Neglect is a visual deficit characterized by complete disinterest towards one side of the visual field.

Macular edema: blurred vision and colour alteration
From image distortion to loss of vision: the effects of macular edema.




